import geopandas as gpd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from cityseer.metrics import networks
from cityseer.tools import graphs, ioAngular distance network centrality
Calculate angular (geometric or “simplest”) distance centralities from a geopandas GeoDataFrame.
Prepare the network as shown in other examples. Working with the dual graph is recommended.
streets_gpd = gpd.read_file("data/madrid_streets/street_network.gpkg")
streets_gpd = streets_gpd.explode(reset_index=True)
G = io.nx_from_generic_geopandas(streets_gpd)
G_dual = graphs.nx_to_dual(G)100%|██████████| 47155/47155 [00:03<00:00, 12720.48it/s]
INFO:cityseer.tools.graphs:Merging parallel edges within buffer of 1.
100%|██████████| 47129/47129 [00:00<00:00, 165486.83it/s]
INFO:cityseer.tools.graphs:Converting graph to dual.
INFO:cityseer.tools.graphs:Preparing dual nodes
100%|██████████| 47129/47129 [00:00<00:00, 78803.24it/s]
INFO:cityseer.tools.graphs:Preparing dual edges (splitting and welding geoms)
100%|██████████| 47129/47129 [00:24<00:00, 1891.03it/s]Use network_structure_from_nx from the cityseer package’s io module to prepare the GeoDataFrames and NetworkStructure.
# prepare the data structures
nodes_gdf, _edges_gdf, network_structure = io.network_structure_from_nx(
G_dual,
)INFO:cityseer.tools.io:Preparing node and edge arrays from networkX graph.
100%|██████████| 47129/47129 [00:00<00:00, 111968.00it/s]
100%|██████████| 47129/47129 [00:06<00:00, 7026.89it/s]
INFO:cityseer.graph:Edge R-tree built successfully with 104026 items.Use the node_centrality_simplest function from the cityseer package’s networks module to calculate shortest angular (geometric or “simplest”) distance centralities. The function requires a NetworkStructure and nodes GeoDataFrame prepared with the network_structure_from_nx function in the previous step.
The function can calculate centralities for numerous distances at once via the distances parameter, which accepts a list of distances.
The function returns the nodes GeoDataFrame with the outputs of the centralities added as columns. The columns are named cc_{centrality}_{distance}_ang. Standard geopandas functionality can be used to explore, visualise, or save the results. See the documentation for more information on the available centrality formulations.
distances = [500, 2000]
nodes_gdf = networks.node_centrality_simplest(
network_structure=network_structure,
nodes_gdf=nodes_gdf,
distances=distances,
)
nodes_gdf.head()INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks:Computing simplest path node centrality.
100%|██████████| 47129/47129 [00:02<00:00, 16162.99it/s]
INFO:cityseer.config:Metrics computed for:
INFO:cityseer.config:Distance: 500m, Beta: 0.008, Walking Time: 6.25 minutes.
INFO:cityseer.config:Distance: 2000m, Beta: 0.002, Walking Time: 25.0 minutes.| ns_node_idx | x | y | live | weight | primal_edge | primal_edge_node_a | primal_edge_node_b | primal_edge_idx | dual_node | cc_density_500_ang | cc_density_2000_ang | cc_harmonic_500_ang | cc_harmonic_2000_ang | cc_hillier_500_ang | cc_hillier_2000_ang | cc_farness_500_ang | cc_farness_2000_ang | cc_betweenness_500_ang | cc_betweenness_2000_ang | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x454839.5-y4476885.3_x454855.9-y4476818.6_k0 | 0 | 454848.067543 | 4.476852e+06 | True | 1 | LINESTRING (454855.9 4476818.6, 454849.1 44768... | x454855.9-y4476818.6 | x454839.5-y4476885.3 | 0 | POINT (454848.067543 4476852.042507) | 29.0 | 142.0 | 12.706080 | 28.091787 | 10.318830 | 19.212521 | 81.501488 | 1049.523926 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| x454833.6-y4476910.5_x454839.5-y4476885.3_k0 | 1 | 454836.577015 | 4.476898e+06 | True | 1 | LINESTRING (454839.5 4476885.3, 454838 4476891... | x454839.5-y4476885.3 | x454833.6-y4476910.5 | 0 | POINT (454836.577015 4476897.9067) | 31.0 | 149.0 | 14.159681 | 30.286549 | 10.620751 | 19.964184 | 90.483238 | 1112.041504 | 136.0 | 968.0 |
| x454839.5-y4476885.3_x454877.1-y4476893.6_k0 | 2 | 454858.300000 | 4.476889e+06 | True | 1 | LINESTRING (454839.5 4476885.3, 454877.1 44768... | x454839.5-y4476885.3 | x454877.1-y4476893.6 | 0 | POINT (454858.3 4476889.45) | 30.0 | 147.0 | 11.984071 | 25.849545 | 9.246469 | 17.739483 | 97.334457 | 1218.130249 | 106.0 | 752.0 |
| x454823.1-y4476952.1_x454833.6-y4476910.5_k0 | 3 | 454828.362585 | 4.476931e+06 | True | 1 | LINESTRING (454833.6 4476910.5, 454830.4 44769... | x454833.6-y4476910.5 | x454823.1-y4476952.1 | 0 | POINT (454828.362585 4476931.303206) | 31.0 | 153.0 | 14.340057 | 31.018009 | 10.690478 | 20.363121 | 89.893082 | 1149.578247 | 165.0 | 1180.0 |
| x454758.1-y4476894.6_x454833.6-y4476910.5_k0 | 4 | 454795.845199 | 4.476903e+06 | True | 1 | LINESTRING (454758.1 4476894.6, 454769.8 44768... | x454833.6-y4476910.5 | x454758.1-y4476894.6 | 0 | POINT (454795.845199 4476902.571916) | 30.0 | 145.0 | 9.221881 | 22.939749 | 7.992776 | 17.387476 | 112.601677 | 1209.203735 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
nodes_gdf.columnsIndex(['ns_node_idx', 'x', 'y', 'live', 'weight', 'primal_edge',
'primal_edge_node_a', 'primal_edge_node_b', 'primal_edge_idx',
'dual_node', 'cc_density_500_ang', 'cc_density_2000_ang',
'cc_harmonic_500_ang', 'cc_harmonic_2000_ang', 'cc_hillier_500_ang',
'cc_hillier_2000_ang', 'cc_farness_500_ang', 'cc_farness_2000_ang',
'cc_betweenness_500_ang', 'cc_betweenness_2000_ang'],
dtype='object')nodes_gdf["cc_betweenness_2000_ang"].describe()count 47129.000000
mean 8083.850098
std 15415.607422
min 0.000000
25% 374.000000
50% 2210.000000
75% 8528.000000
max 227236.000000
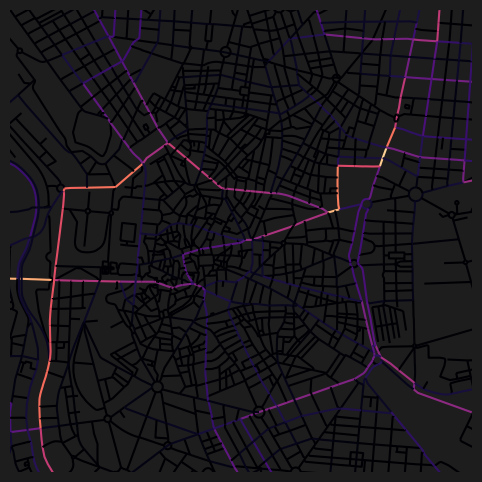
Name: cc_betweenness_2000_ang, dtype: float64fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 6), facecolor="#1d1d1d")
nodes_gdf.plot(
column="cc_harmonic_500_ang",
cmap="magma",
legend=False,
ax=ax,
)
ax.set_xlim(438500, 438500 + 3500)
ax.set_ylim(4472500, 4472500 + 3500)
ax.axis(False)(np.float64(438500.0),
np.float64(442000.0),
np.float64(4472500.0),
np.float64(4476000.0))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 6), facecolor="#1d1d1d")
nodes_gdf.plot(
column="cc_betweenness_2000_ang",
cmap="magma",
legend=False,
ax=ax,
)
ax.set_xlim(438500, 438500 + 3500)
ax.set_ylim(4472500, 4472500 + 3500)
ax.axis(False)(np.float64(438500.0),
np.float64(442000.0),
np.float64(4472500.0),
np.float64(4476000.0))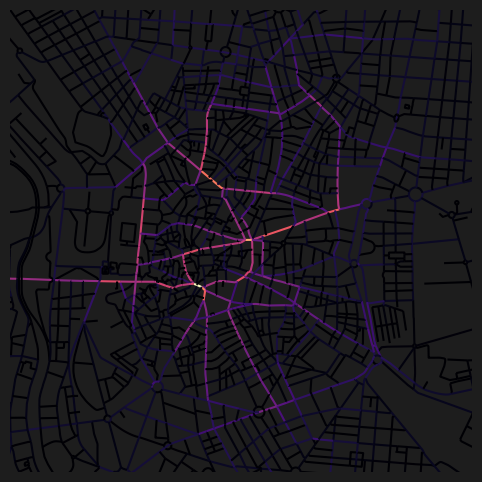
Alternatively, you can define the distance thresholds using a list of minutes instead.
nodes_gdf = networks.node_centrality_simplest(
network_structure=network_structure,
nodes_gdf=nodes_gdf,
minutes=[15],
)INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks:Computing simplest path node centrality.
100%|██████████| 47129/47129 [00:01<00:00, 26462.19it/s]
INFO:cityseer.config:Metrics computed for:
INFO:cityseer.config:Distance: 1200m, Beta: 0.00333, Walking Time: 15.0 minutes.The function will map the minutes values into the equivalent distances, which are reported in the logged output.
nodes_gdf.columnsIndex(['ns_node_idx', 'x', 'y', 'live', 'weight', 'primal_edge',
'primal_edge_node_a', 'primal_edge_node_b', 'primal_edge_idx',
'dual_node', 'cc_density_500_ang', 'cc_density_2000_ang',
'cc_harmonic_500_ang', 'cc_harmonic_2000_ang', 'cc_hillier_500_ang',
'cc_hillier_2000_ang', 'cc_farness_500_ang', 'cc_farness_2000_ang',
'cc_betweenness_500_ang', 'cc_betweenness_2000_ang',
'cc_density_1200_ang', 'cc_harmonic_1200_ang', 'cc_hillier_1200_ang',
'cc_farness_1200_ang', 'cc_betweenness_1200_ang'],
dtype='object')As per the function logging outputs, 15 minutes has been mapped to 1200m at default speed_m_s, so the corresponding outputs can be visualised using the 1200m columns. Use the configurable speed_m_s parameter to set a custom metres per second walking speed.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 6), facecolor="#1d1d1d")
nodes_gdf.plot(
column="cc_harmonic_1200_ang",
cmap="magma",
legend=False,
ax=ax,
)
ax.set_xlim(438500, 438500 + 3500)
ax.set_ylim(4472500, 4472500 + 3500)
ax.axis(False)(np.float64(438500.0),
np.float64(442000.0),
np.float64(4472500.0),
np.float64(4476000.0))
Adaptive centrality for larger distances
For larger distance thresholds, the computational cost increases substantially. The node_centrality_simplest_adaptive function uses an adaptive sampling strategy to compute centralities more efficiently at larger scales while maintaining statistical accuracy.
The target_rho parameter controls the correlation target between the sampled and full computations. A value of 0.95 means the function aims for at least 95% correlation with the exact computation. The function automatically determines which distances require sampling versus full computation, and reports the expected correlation for each distance.
distances = [500, 2000, 5000, 10000]
nodes_gdf = networks.node_centrality_simplest_adaptive(
network_structure=network_structure,
nodes_gdf=nodes_gdf,
distances=distances,
target_rho=0.95,
)
nodes_gdf.columnsINFO:cityseer.metrics.networks:Computing adaptive simplest path node centrality.
INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks:Probing reachability (50 samples)...
INFO:cityseer.config:
INFO:cityseer.config:Adaptive sampling plan (target ρ ≥ 0.95, internal target 0.97 for both metrics):
INFO:cityseer.config: Distance │ Reach │ Sample p │ Expected ρ
INFO:cityseer.config: ─────────┼────────┼──────────┼───────────
INFO:cityseer.config: 500m │ 88 │ full │ 1.00 (exact)
INFO:cityseer.config: 2000m │ 1178 │ full │ 1.00 (exact)
INFO:cityseer.config: 5000m │ 6499 │ 24% │ 0.97 (eff_n=1561)
INFO:cityseer.config: 10000m │ 21665 │ 7% │ 0.97 (eff_n=1561)
INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks:Running per-distance centrality...
INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks: 500m: full...
INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks: 2000m: full...
INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks: 5000m: p=24%...
INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks: actual: reach=4976, eff_n=1195, expected ρ=0.96
INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks: 10000m: p=7%...
INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks: actual: reach=16332, eff_n=1177, expected ρ=0.96
INFO:cityseer.metrics.networks:Adaptive centrality complete.Index(['ns_node_idx', 'x', 'y', 'live', 'weight', 'primal_edge',
'primal_edge_node_a', 'primal_edge_node_b', 'primal_edge_idx',
'dual_node', 'cc_density_500_ang', 'cc_density_2000_ang',
'cc_harmonic_500_ang', 'cc_harmonic_2000_ang', 'cc_hillier_500_ang',
'cc_hillier_2000_ang', 'cc_farness_500_ang', 'cc_farness_2000_ang',
'cc_betweenness_500_ang', 'cc_betweenness_2000_ang',
'cc_density_1200_ang', 'cc_harmonic_1200_ang', 'cc_hillier_1200_ang',
'cc_farness_1200_ang', 'cc_betweenness_1200_ang', 'cc_density_5000_ang',
'cc_harmonic_5000_ang', 'cc_farness_5000_ang', 'cc_hillier_5000_ang',
'cc_density_10000_ang', 'cc_harmonic_10000_ang', 'cc_farness_10000_ang',
'cc_hillier_10000_ang', 'cc_betweenness_5000_ang',
'cc_betweenness_10000_ang'],
dtype='object')The adaptive function reports the sampling plan during execution, showing which distances use full computation versus sampling. For shorter distances where the number of reachable nodes is small, full computation is used. For larger distances, the function applies sampling to achieve the target correlation efficiently.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 6), facecolor="#1d1d1d")
nodes_gdf.plot(
column="cc_betweenness_10000_ang",
cmap="magma",
legend=False,
ax=ax,
)
ax.set_xlim(438500, 438500 + 3500)
ax.set_ylim(4472500, 4472500 + 3500)
ax.axis(False)(np.float64(438500.0),
np.float64(442000.0),
np.float64(4472500.0),
np.float64(4476000.0))